Overview
Note: This research was conducted in early 2025 and documented approximately one year later. The repository and notebooks are not fully organized, and some experimental results were lost over time. What remains represents our key findings and published models.
This research explores post-training pruning of Large Language Models, specifically LLaMA model families. We investigated how to efficiently compress LLMs by removing transformer blocks while preserving performance through strategic fine-tuning.
Collaborators: Rahat Kabir, Sharukh Khan
Pruning Methods
We explored multiple approaches to identify and remove redundant layers:
- Magnitude Pruning: Initial experiments with weight magnitude-based pruning before moving to block-level methods
- ShortGPT / Block Importance: Removes transformer blocks based on importance scores
- Angular Distance: Measures block influence by comparing layer input/output angles
- Attention Norm Analysis: Identifies redundant layers through attention weight norms
Key Results
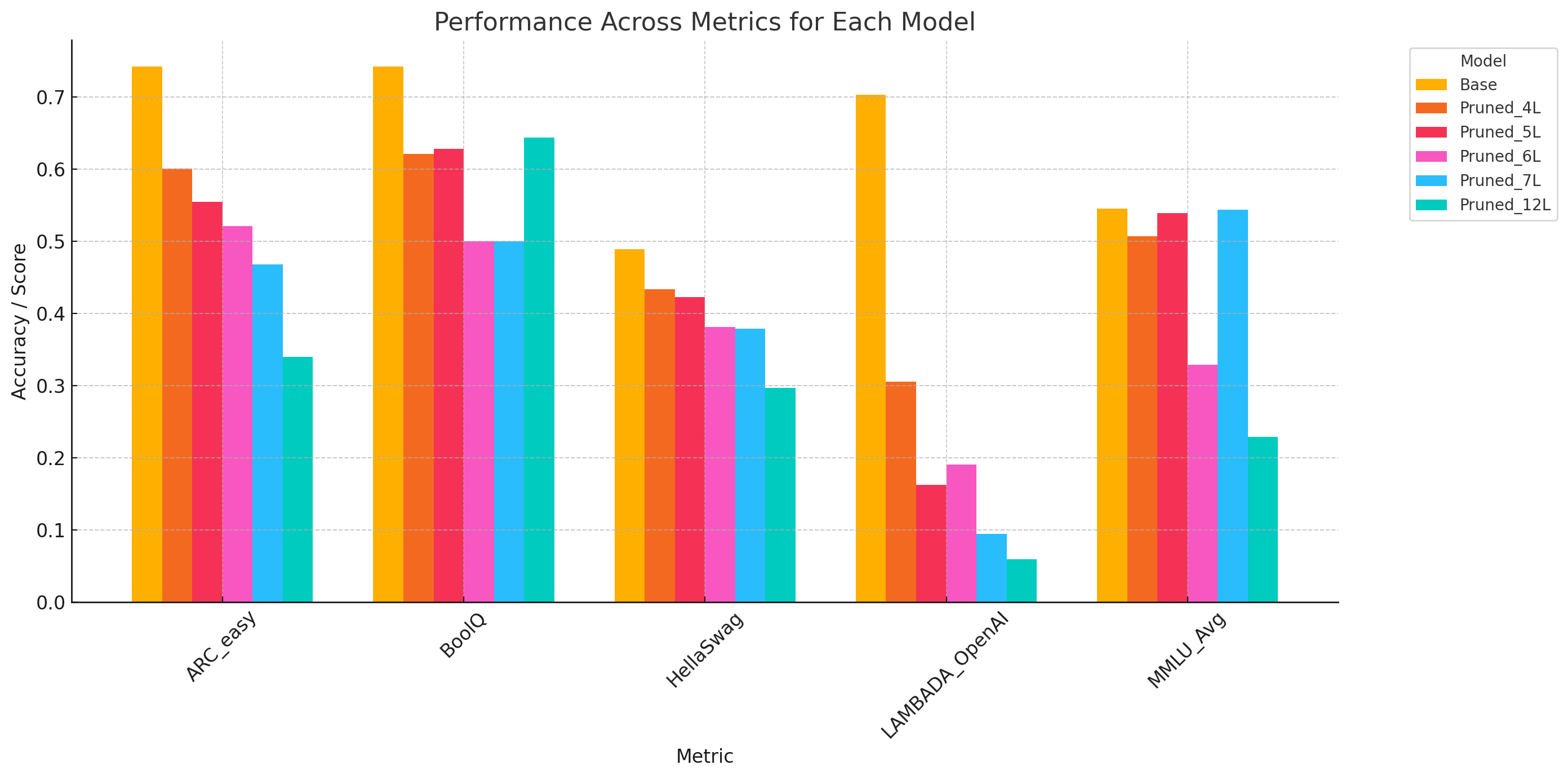
Performance Across Benchmarks
Comparison of base LLaMA 3.2-3B vs pruned variants (4L, 5L, 6L, 7L, 12L removed) across standard benchmarks.
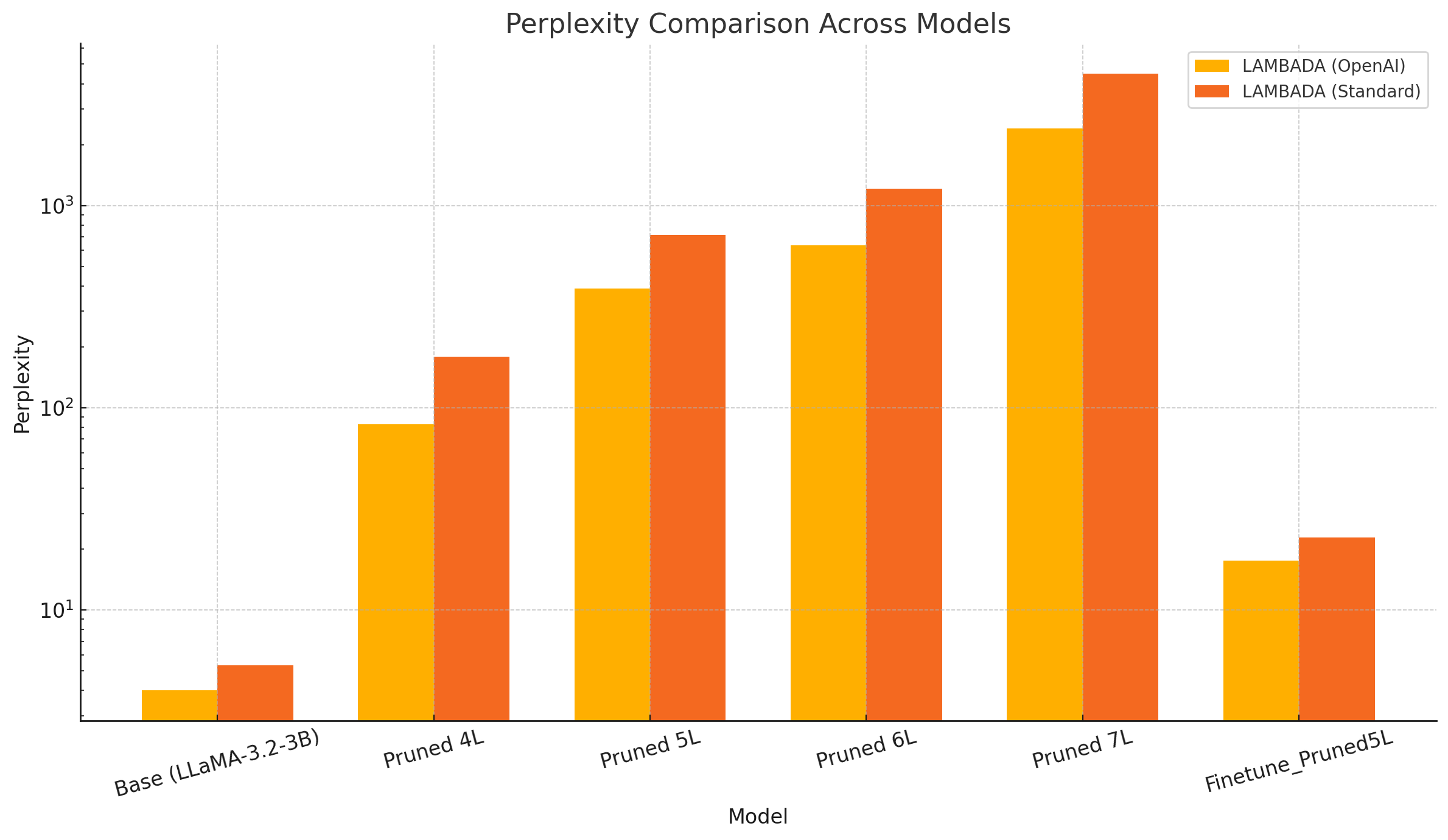
Perplexity Recovery
A critical finding: fine-tuning dramatically recovers perplexity after pruning. The fine-tuned model with 5 layers removed shows significantly lower perplexity than non-finetuned pruned variants.
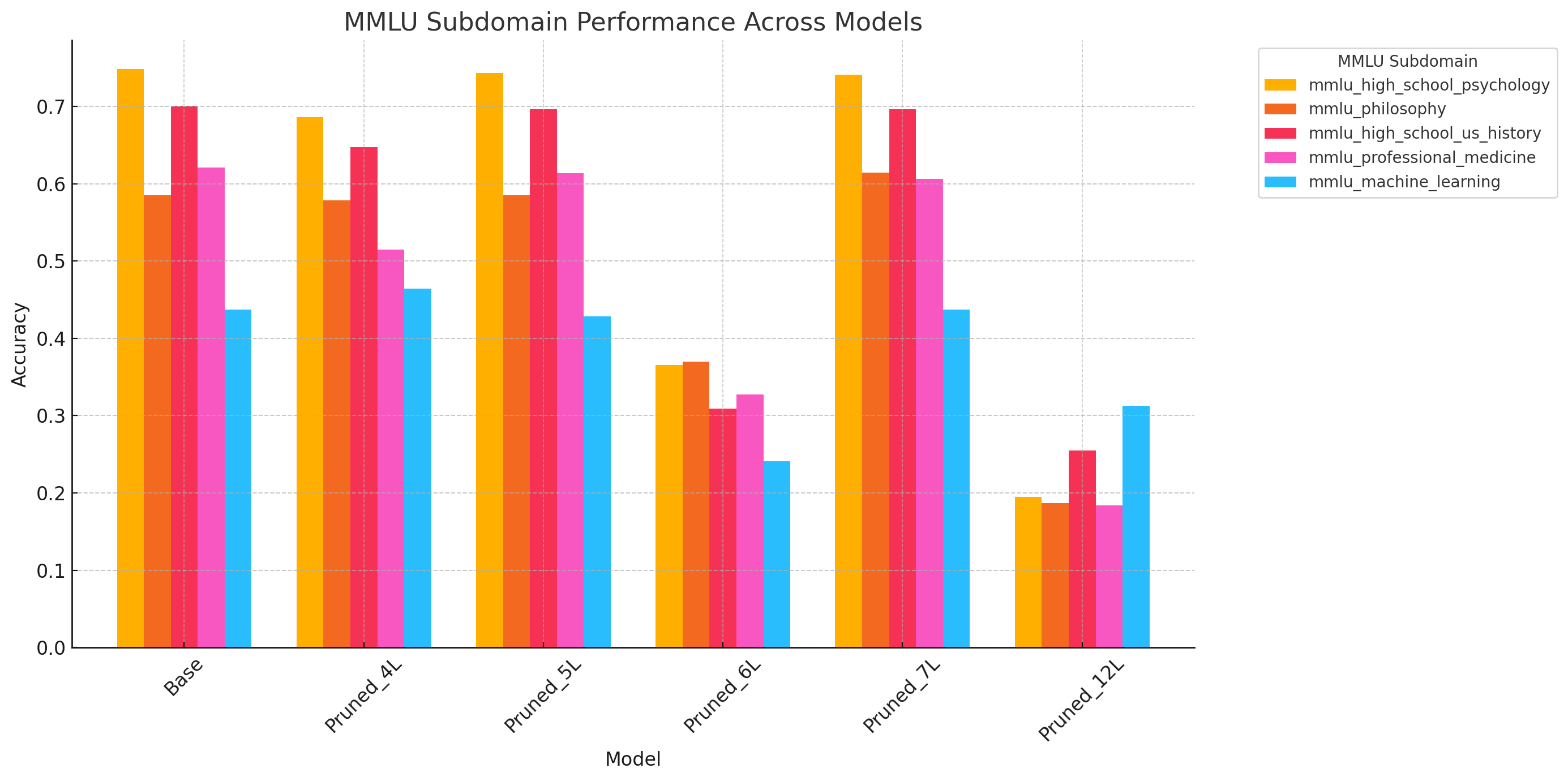
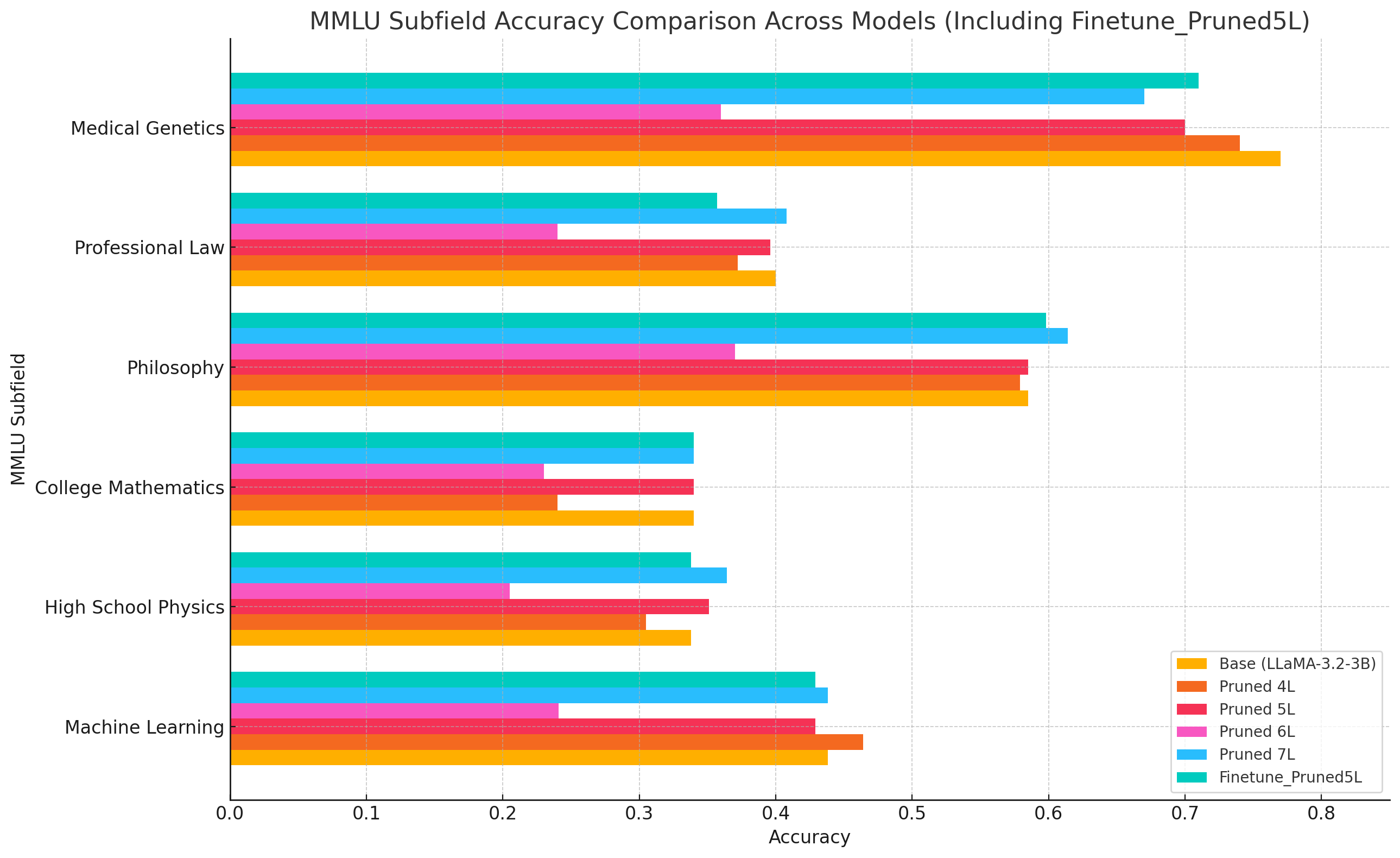
MMLU Subfield Analysis
Detailed performance breakdown across MMLU subfields including Medical Genetics, Professional Law, Philosophy, College Mathematics, High School Physics, and Machine Learning.
Published Models
All pruned models are available on HuggingFace:
- LLaMA 3.2-3B pruned variants (4L, 5L, 6L, 7L, 12L removed)
- LLaMA 3.1-8B pruned variants with angular block influence
- Fine-tuned versions of pruned models
Skills & Knowledge Gained
Through this research, I developed hands-on experience in:
Model Compression & Pruning
- Implementing block/layer removal using importance metrics (ShortGPT, Angular distance, Attention norms)
- Understanding transformer architecture internals and layer redundancy
- Analyzing trade-offs between model size and performance
Fine-Tuning & Recovery
- Applying LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) to recover pruned model performance
- Working with PEFT library for efficient fine-tuning
- Iterating on hyperparameters to optimize recovery
LLM Evaluation
- Benchmarking models using lm-evaluation-harness
- Interpreting results across diverse tasks: HellaSwag, MMLU, ARC, BoolQ, LAMBADA
- Understanding perplexity as a model quality metric
Model Deployment
- Publishing trained models to HuggingFace Hub
- Documenting model cards and usage instructions
- Managing model versions and variants
Technologies
PyTorch, Hugging Face Transformers, PEFT (LoRA), lm-evaluation-harness, Lightning AI, Google Colab, Kaggle
Research conducted: Early 2025 | Documented: January 2026